Kubernetes
Kubernetes (K8s) is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It groups containers that make up an application into logical units for easy management and discovery. Kubernetes provides a framework to run distributed systems resiliently, taking care of scaling and failover for your applications.
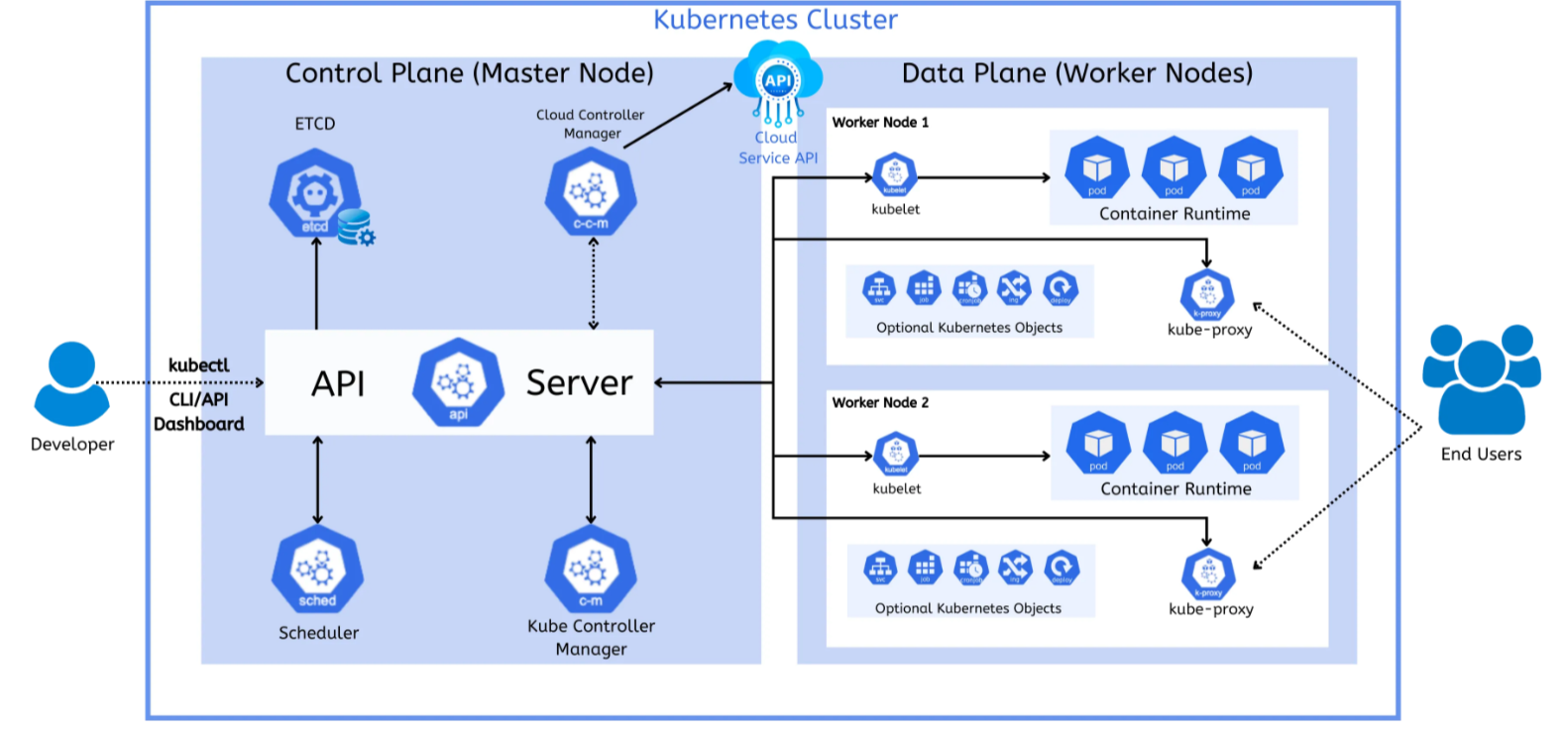
Kubernetes cluster architecture
Components and Terminology
Pod - a pod is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes, and is the basic building block of your application. A pod is a collection of one or more containers, with shared storage and network resources, and a specification for how to run the containers.
Namespace - a namespace is a logical grouping of resources in a cluster
Secret - a secret is an object that contains sensitive information such as passwords, API keys, and certificates
ConfigMap - a configmap is an object that contains configuration information for an application (as key-value pairs)
Deployment - a Deployment manages a set of Pods to run an application workload, usually one that doesn’t maintain state
Service - a service is an object (the same way that a Pod or a ConfigMap is an object). Since Pods are ephemeral (they can be restarted, moved to another node, or replaced), a Service ensures that applications can always reach the right Pods even if their IP addresses change.
Kubectl
Kubectl is a command-line tool for controlling the Kubernetes cluster. It allows you to manage your cluster and applications through the Kubernetes API.
Note
Kubernetes config files are stored in the .kube directory of the user’s home directory.
Commands
kubectl get nodes- list all nodes in the clusterkubectl create namespace <namespace>- create a new namespace (more info)kubectl get namespace- list all namespaces in the clusterkubectl apply -n <namespace> -f <filename>- apply a configuration to a namespace (e.g. kubectl apply -n my-namespace -f configmaps/my-configmap.yaml) (more info)