Deep Learning
Deep learning is a method in artificial intelligence (AI) that teaches computers to process data in a way that is inspired by the human brain. Deep learning models can recognize complex patterns in pictures, text, sounds, and other data to produce accurate insights and predictions
deep learning algorithms can be regarded both as a sophisticated and mathematically complex evolution of machine learning algorithms
Describes algorithms that analyze data with a logic structure similar to how a human would draw conclusions.
Can be supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, self-supervised, or reinforcement.
To achieve this deep learning applications use a layered structure of algorithms called an artificial neural network (ANN).
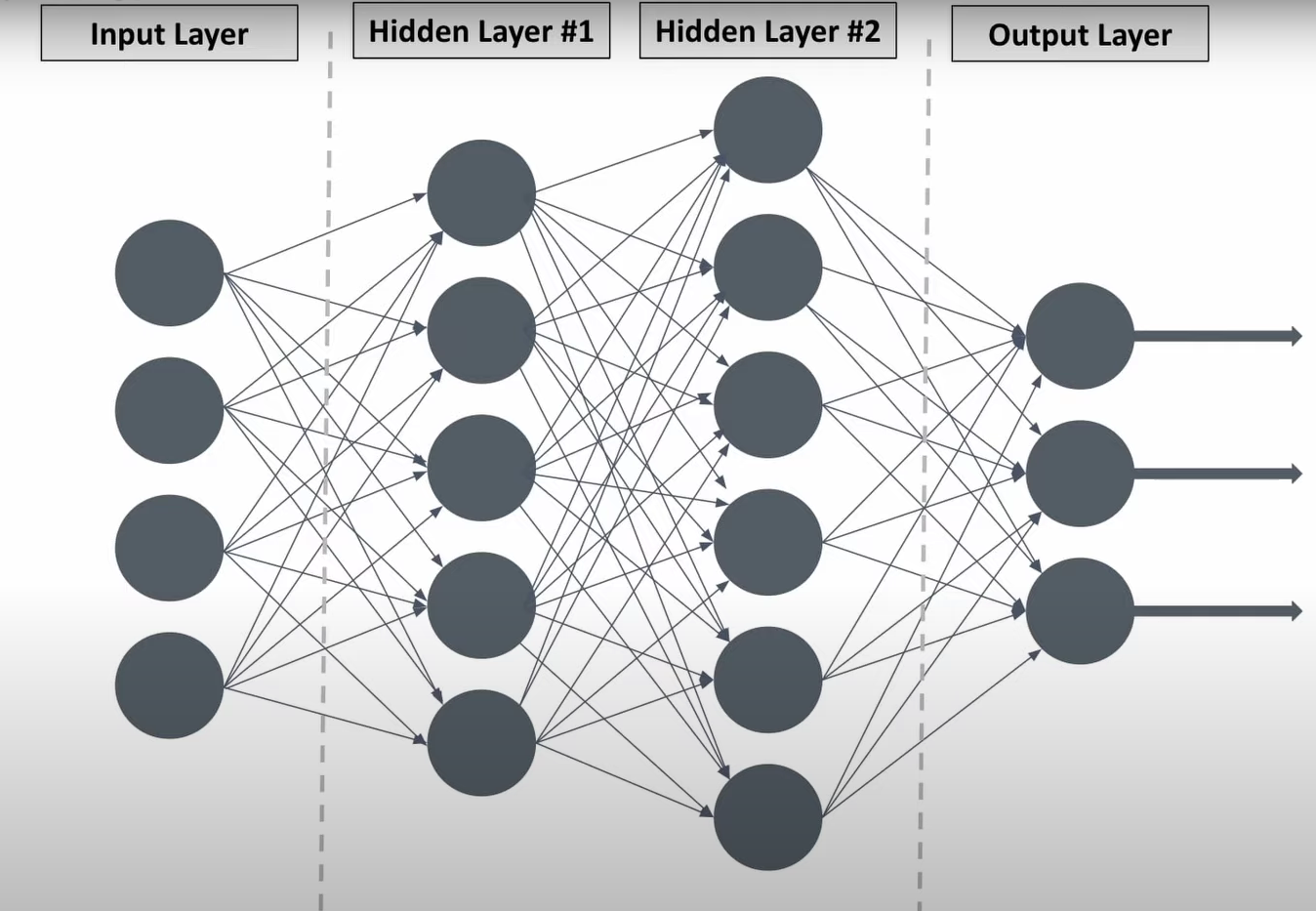
Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
Hidden layers are called hidden, because their values aren’t directly observed in the training data (they are calculated during the training process).
In simple terms, the hidden layers are calculated values used by the network to make predictions.
The more hidden layers a network has, the more complex the patterns it can recognize.
ANNs are hungry for data. The more data you feed them, the better they perform.
Advantages of deep learning:
Automatic feature extraction (no need to manually define features)
High accuracy
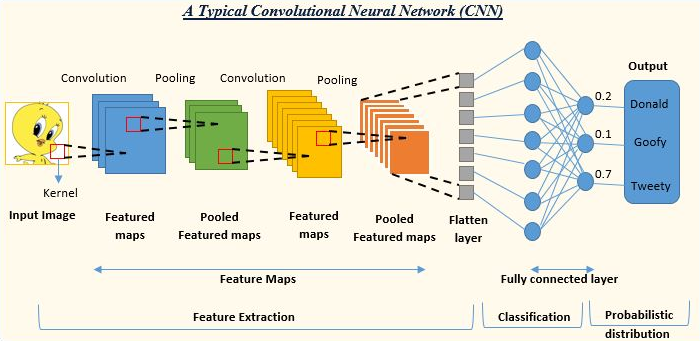
CNN (Convolutional Neural Network)
CNNs are a type of deep learning neural network that have been successfully applied to analyzing visual imagery.