VNC (Virtual Network Computing)
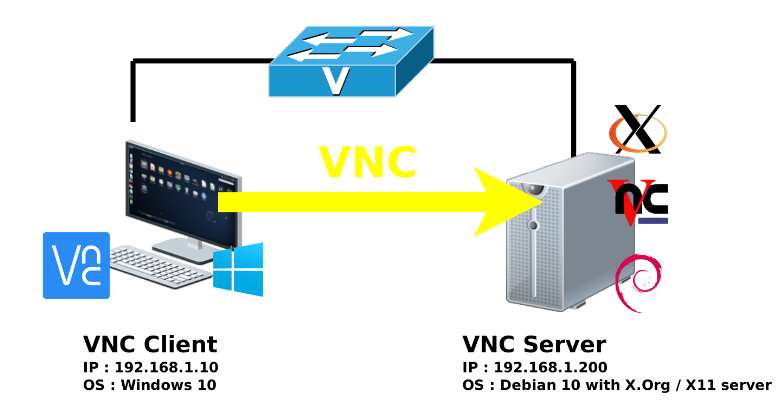
VNC is a protocol that allows a desktop to be viewed and controlled remotely over the Internet. It is similar to Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). VNC is platform-independent and can be used to view a desktop from a variety of operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X. It is also compatible with several mobile operating systems, such as Android and iOS.
VNC Server
VNC server is a program that shares a desktop with other computers over the Internet. E.g. TightVNC, RealVNC, UltraVNC, TigerVNC, etc.
Ports 5900 and 5901 are used by default for VNC server.
Server and client communicate using RFB (Remote Frame Buffer) protocol.
VNC client
VNC client is a program that connects to a remote computer. E.g. TightVNC, RealVNC, UltraVNC, TigerVNC, etc. Client sends keyboard and mouse events to the server, receives updates to the screen in return, and draws these updates on the screen.
noVNC
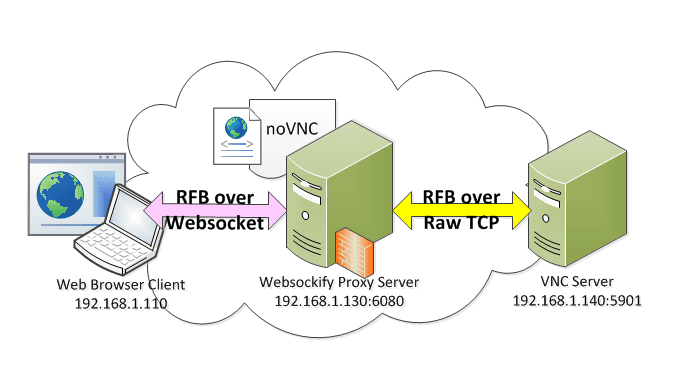
noVNC - the open source VNC client - noVNC is both a VNC client JavaScript library as well as an application built on top of that library. noVNC runs well in any modern browser including mobile browsers (iOS and Android).
RFB over WebSockets (RFC 6455) is used to communicate between the client and server.
Port 6080 is used by default for noVNC Websockify server.
Websockify is a WebSocket to TCP proxy/bridge. It accepts WebSocket connections and forwards them to a specified host and port, which is typically the VNC server.
Popular noVNC